What we offer for you!
Welcome to ARTin Company, where excellence in design and construction meets innovation and expertise. Established in 2012, ARTin Company began its journey with a strong focus on civil engineering projects. Over the years, our dedication to quality and precision has earned us certification from the Iranian Ministry of Roads and City Planning, enabling us to expand our horizons and offer a comprehensive range of construction services.
Today, ARTin Company is proud to be at the forefront of the construction industry, actively engaged in a variety of ongoing projects across multiple sectors. Our portfolio showcases not only our versatility but also our commitment to delivering outstanding results on every project we undertake. From intricate civil engineering tasks to large-scale construction developments, our team has the knowledge, experience, and resources to bring any vision to life.
At the core of our success is a leadership team of four highly skilled head engineers, whose expertise and innovative approach drive the company forward. Complemented by a network of dedicated subcontractor teams, we ensure that each project is executed with precision, efficiency, and the highest standards of craftsmanship.
Our design and construction services are tailored to meet the unique needs of our clients, whether it’s developing state-of-the-art infrastructure or creating aesthetically pleasing and functional spaces. We blend creative design in construction practices to deliver projects that are not only structurally sound but also visually striking.
Explore our Projects page to learn more about our completed and ongoing projects, and discover the talented individuals who make ARTin Company a leader in the industry. We look forward to partnering with you on your next project and turning your ideas into reality.
Step 1
Consultation Service
- Project Planning and Management: Feasibility Studies: Consultants assess the viability of a project before it begins, considering factors like cost, location, materials, and timeline. Project Scheduling: They help develop realistic timelines and milestones. Budgeting and Cost Estimation: Consultants can provide detailed cost estimates and help manage budgets throughout the project.
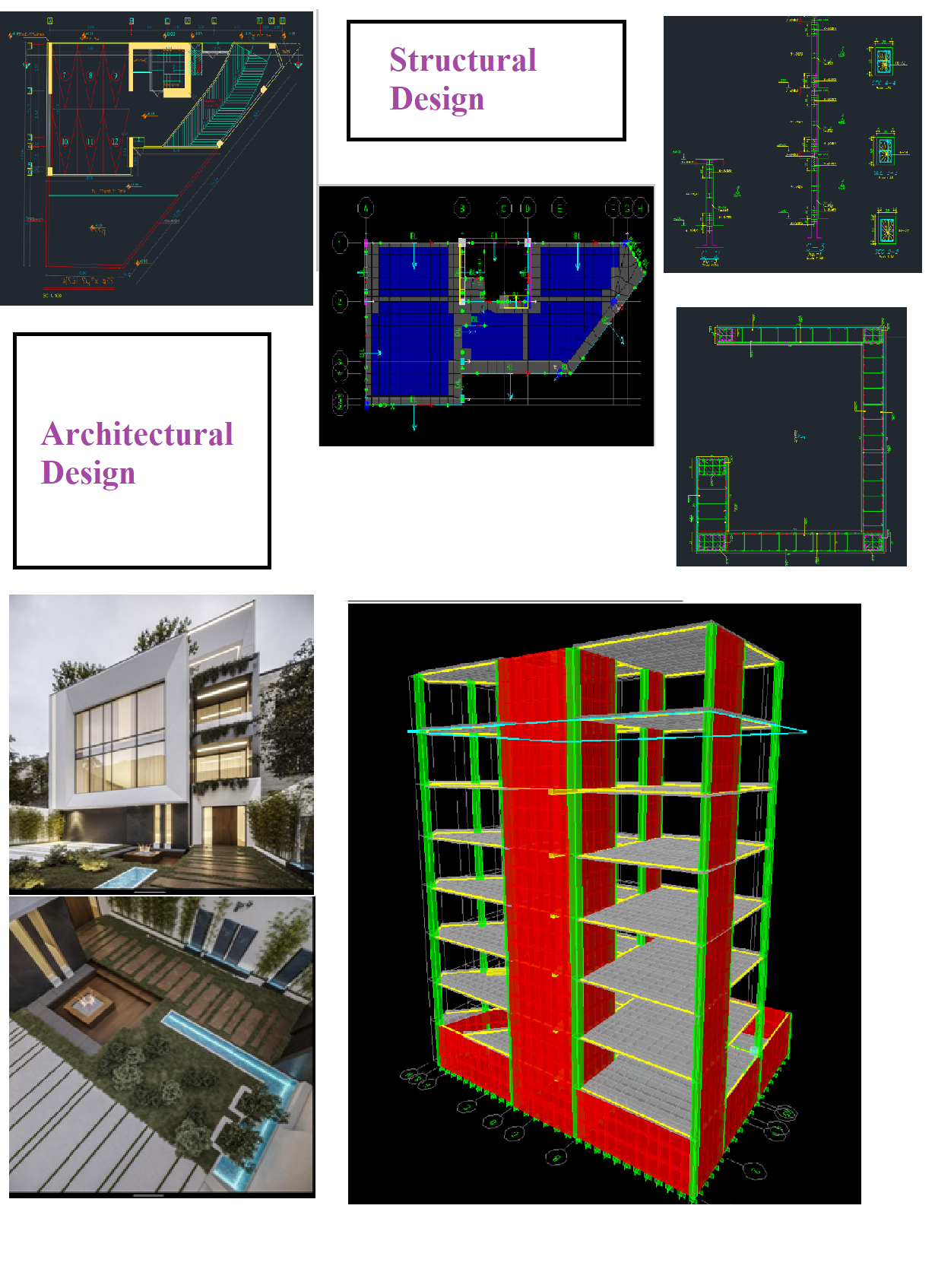
- Design Consultation: Architectural Design: Consultation can include working with architects to refine building designs according to the client’s needs and regulatory requirements. Structural Engineering: Ensuring the structural integrity of the building is critical, and consultants can provide expertise on materials, load-bearing walls, foundation design, etc. Sustainability and Environmental Impact: Consultants help design buildings with energy efficiency and minimal environmental impact, which can include green building practices.
- Regulatory and Compliance Consulting: Building Codes and Permits: Navigating local building codes and obtaining necessary permits is a complex process that consultants can streamline. Safety Standards: Ensuring that the project complies with health and safety regulations is another critical role of consultants.
- Construction Phase Consultation: Quality Control: Consultants may be involved in monitoring the construction to ensure that it meets the specified standards and quality. Site Supervision: They can provide on-site management to ensure that the project is on track and that any issues are quickly resolved. Contract Management: Consultants can manage relationships with contractors, ensuring that all parties adhere to the terms of their agreements.
- Specialized Consultation: Risk Management: Identifying potential risks and creating strategies to mitigate them is a vital service. Dispute Resolution: If conflicts arise between parties involved in the construction, consultants can act as mediators. Technology Integration: Advising on the use of modern construction technologies, such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), can improve project outcomes.
- Post-Construction Services: Final Inspections: Consultants conduct final inspections to ensure everything is completed to the required standard. Handover Documentation: Preparing and managing the documentation required for project handover to the client. Maintenance Planning: Advising on the maintenance needs of the building post-construction.
- Consultation for Specific Sectors: Residential Construction: Custom homes, apartments, and housing projects. Commercial Construction: Office buildings, shopping centers, and other commercial properties. Industrial Construction: Factories, warehouses, and other industrial facilities.
Step 2
Construction Service
Feasibility Studies:
Construction in the context of building refers to the process of creating infrastructure, buildings, or other structures. It involves several stages, from planning and design to the actual building process, and finally, completion and handover. Here’s a detailed explanation of the construction process in the building industry:
1. Planning and Design
Initial Planning: The construction process begins with an idea or need, which is then developed into a plan. This stage involves identifying the purpose of the building, its location, and the basic requirements.
Feasibility Study: A feasibility study is conducted to determine whether the project is viable in terms of cost, technical requirements, and regulatory compliance.
Design Phase:
Architectural Design: Architects create detailed drawings and models that outline the structure’s appearance, layout, and functionality.
Engineering Design: Structural engineers ensure that the building is safe and stable, while mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) engineers design the necessary systems within the building.
2. Pre-Construction
Permitting and Approvals: Before construction can begin, all necessary permits and approvals must be obtained from local authorities. This ensures that the building complies with zoning laws, building codes, and environmental regulations.
Site Preparation:
Clearing and Excavation: The construction site is cleared of any existing structures, vegetation, and debris. Excavation is done to prepare for the foundation.
Setting Out: The exact location of the building is marked on the ground using stakes or other markers.
3. Foundation
Types of Foundations: Depending on the soil condition and building design, different types of foundations may be used, such as slab-on-grade, crawl space, or basement foundations.
Construction of Foundation: Concrete is typically poured into trenches or forms to create a stable base for the building. Reinforcement, such as steel rebar, is often used to add strength.
4. Superstructure Construction
Framing: The framing phase involves constructing the skeleton of the building. This includes the erection of walls, floors, and roof structures. Materials used may include wood, steel, or concrete.
Roofing: Once the frame is complete, the roof is constructed. This may involve installing trusses, laying roofing materials (such as shingles or metal sheets), and waterproofing.
Exterior Walls and Facade: The exterior walls are built and the building’s facade is completed. This includes adding insulation, windows, doors, and any exterior finishes like brick, siding, or stucco.
5. Interior Construction
Partition Walls: Interior walls and partitions are constructed to divide the space into rooms and different functional areas.
Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing (MEP) Installation:
Electrical Wiring: Electricians install wiring, outlets, switches, and lighting fixtures.
Plumbing: Plumbers install pipes, fixtures, and systems for water supply, drainage, and sewage.
HVAC Systems: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems are installed to control the building’s climate.
6. Finishing Work
Interior Finishes: This includes installing drywall, flooring (such as tiles, wood, or carpet), and painting walls and ceilings.
Fixtures and Fittings: Cabinets, countertops, appliances, and other fixtures are installed. This also includes bathroom fixtures like sinks, toilets, and showers.
Final Inspections: Before the building is occupied, final inspections are carried out to ensure that all work complies with building codes and standards.
7. Post-Construction
Handover: Once the construction is completed, the building is handed over to the owner or client. This includes transferring all relevant documents, such as warranties, manuals, and as-built drawings.
Maintenance and Operations: After handover, the building enters the operational phase, where regular maintenance is required to keep the building in good condition. This may involve routine inspections, repairs, and updates.
8. Project Closeout
Punch List: A punch list is created, listing any minor tasks or corrections that need to be completed before final acceptance.
Final Payment: The final payment is made after the project owner is satisfied with the completed work
